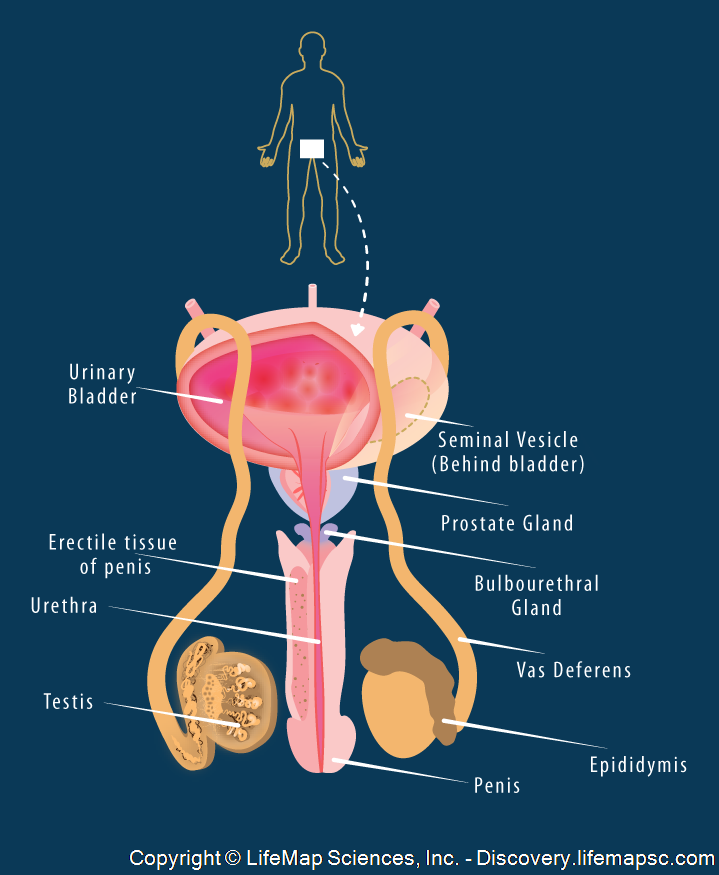
Schematic presentation of the male reproductive organs.
Sperm cells are produced in the testes, which are located in the scrotum. From there, sperm are transferred to the epididymis, coiled tubules, which store sperm and are the site of their final maturation.
During ejaculation, sperm cells are forced up into the vasa deferentia, which elongate up from the epididymis to behind the bladder. The ends of the vasa deferentia are called the ejaculatory ducts.
The seminal vesicles, located behind the bladder, produce seminal fluid which contains mucus, amino acids, fructose as the energy source for the sperm, and prostaglandins. The seminal vesicles empty into the ejaculatory ducts, which empty into the urethra.
The prostate gland secretes alkaline secretions directly into the urethra, to buffer any residual urine.
The bulbourethral glands (Cowper’s glands) are a small pair of glands along the urethra, below the prostate, which secrete lubricant fluid just before emission of the semen.
The urethra passes through the penis.
In humans, the penis contains three cylinders of spongy, erectile tissue.



