Sources for Cell Therapy
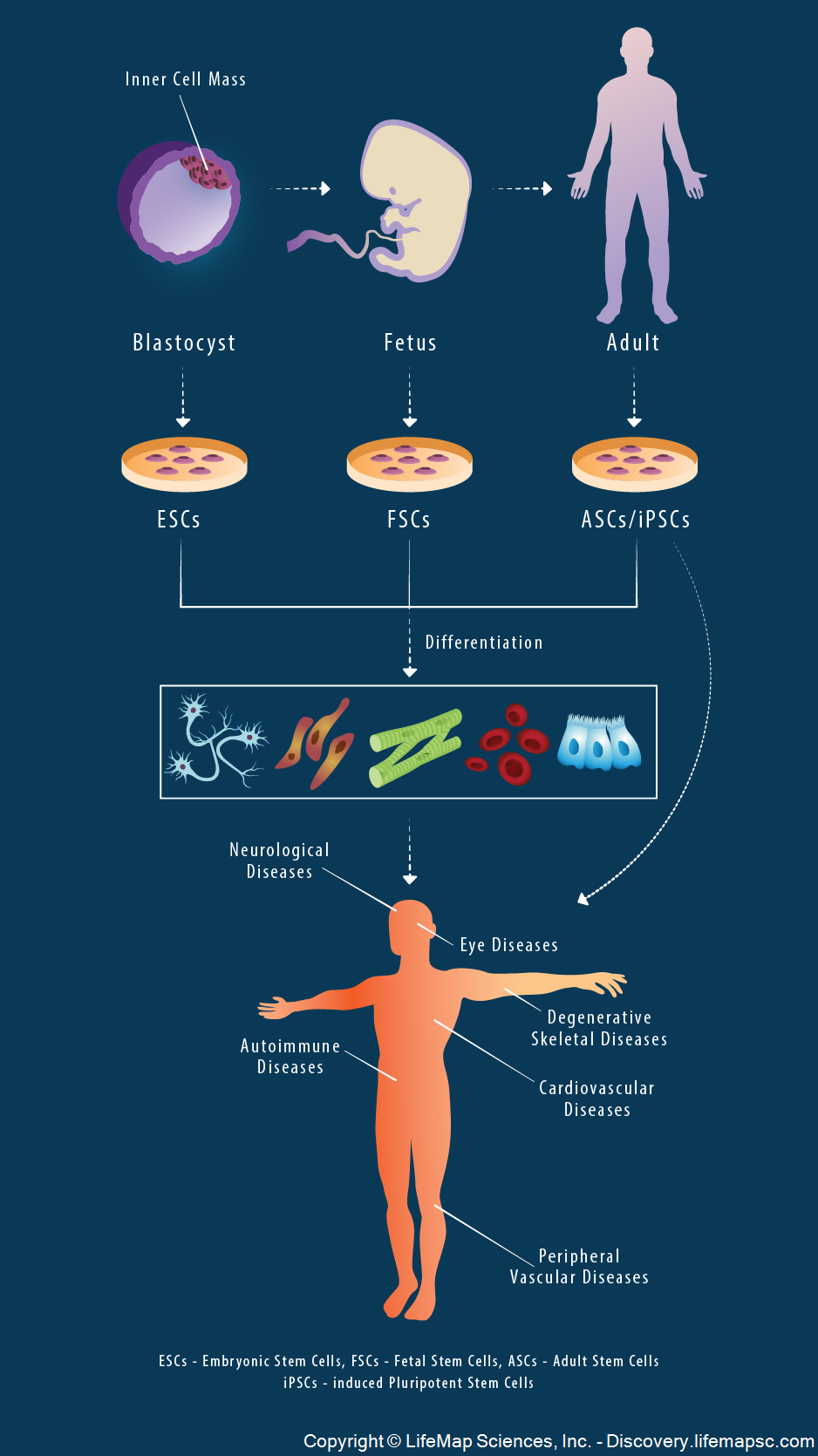
Numerous cell sources can be utilized for cell therapies: embryonic stem cells (ESCs) isolated from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst, fetal stem/progenitor cells (FSCs) isolated from fetal tissues, adult stem/progenitor cells (ASCs) or primary cells derived from adult tissues, and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) reprogrammed from somatic cells under specific conditions. Following isolation, any of these cell types can be cultured and expanded, and potentially differentiated or genetically manipulated to obtain the desired cell type. The resulting cells can be reintroduced to the patient's body to treat neurological, cardiovascular, degenerative skeletal and other diseases.



