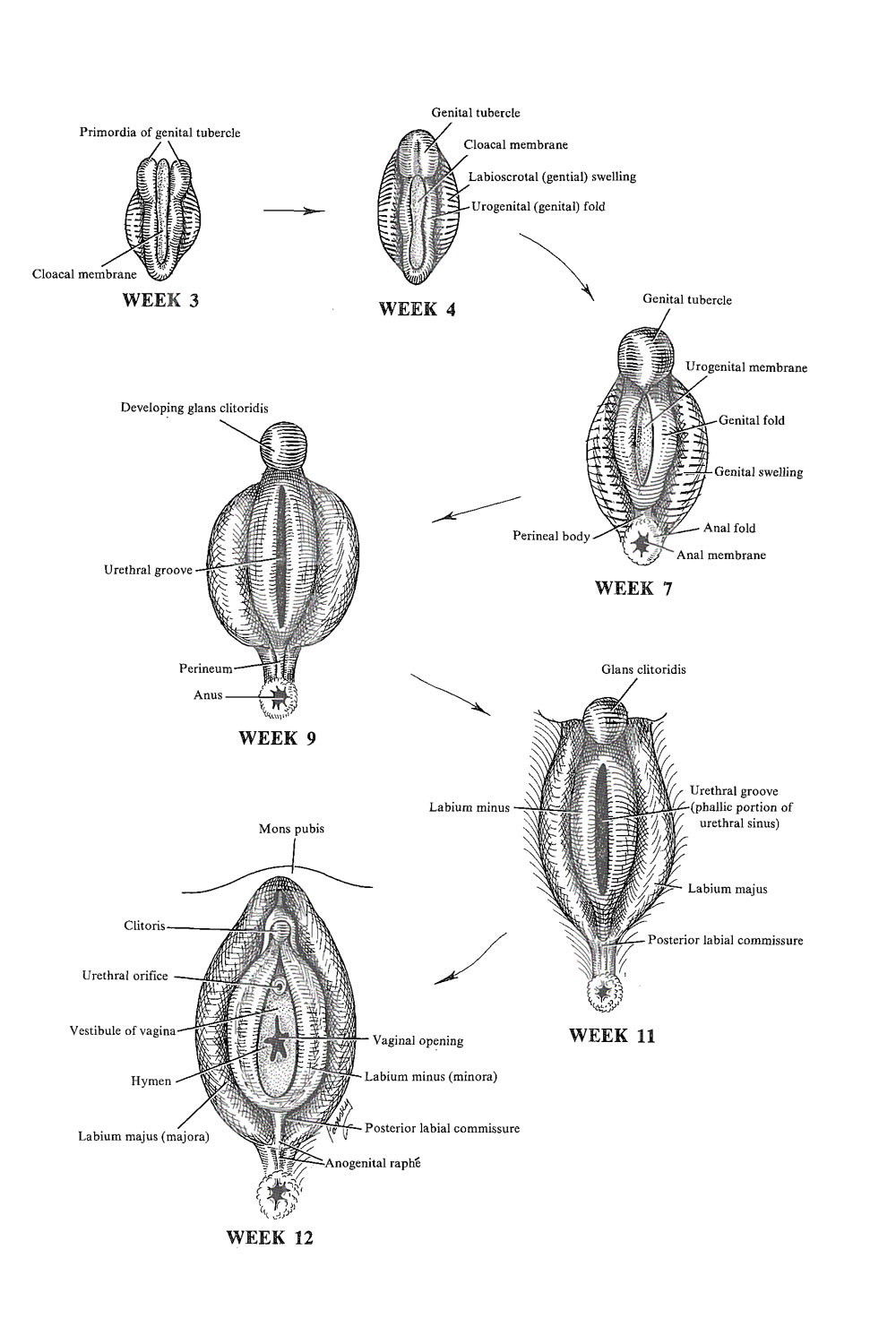
107. Development of The Female External Genital Organs
Review of MEDICAL EMBRYOLOGY Book by BEN PANSKY, Ph.D, M.D.
- The indifferent stage: see Section 98 for description
- Definitive development: in the absence of androgens, feminization of the indifferent external genitalia takes place
- THE CLOACAL MEMBRANE, by week 3, is very extensive, and its anterior end is level with the base of the umbilical cord
- It is at this stage that the cloacal membrane is bordered laterally by 2 mesenchymal projections, covered by ectoderm, which are the paired primordia of the genital tubercle
- At week 4, the anterior end of the cloacal membrane retracts from the base of the umbilical cord, permitting formation of the anterior body wall below (caudal to) the umbilicus, and the paired primordia of the genital tubercle come together in the midline to form the genital tubercle
- The cloacal fold, which surrounds the cloacal membrane, further prolongs the genital tubercle, and about this time new swellings appear, the genital swellings, on either side of the cloacal folds and surround the genital tubercle and the cloacal folds
- At week 7, the cloacal membrane is divided into the urogenital membrane (anteriorly) and the anal membrane (posteriorly), separated by the perineal body (perineum)
- The cloacal fold is divided into the genital fold, which surrounds the urogenital membrane, and the anal fold, which circumscribes the ectodermal depression of the proctodeum covered by the anal membrane
- THE UROGENITAL MEMBRANE, in week 9, disappears, thus, the phallic segment of the urogenital sinus becomes open to the exterior
- DIFFERENTIATION OF THE EXTERNAL GENITALIA takes place during month 3 and closely follows the pattern of the primitive structures
- The genital tubercle elongates only slightly and forms the clitoris, where erectile tissues develop
- The urogenital sinus remains open with the urethra opening anteriorly and the vagina posteriorly, within the interior of the vestibule portion of the sinus
- The vestibule is bordered laterally by the genital folds, which become the labia minora
- The genital (labioscrotal) swellings largely remain unfused and form the labia majora
- They do fuse posteriorly to form the posterior labial commissure and anteriorly to form the elevation known as the mons pubis