90. Congenital Malformations of Digestive System: Hindgut Malformations
Review of MEDICAL EMBRYOLOGY Book by BEN PANSKY, Ph.D, M.D.
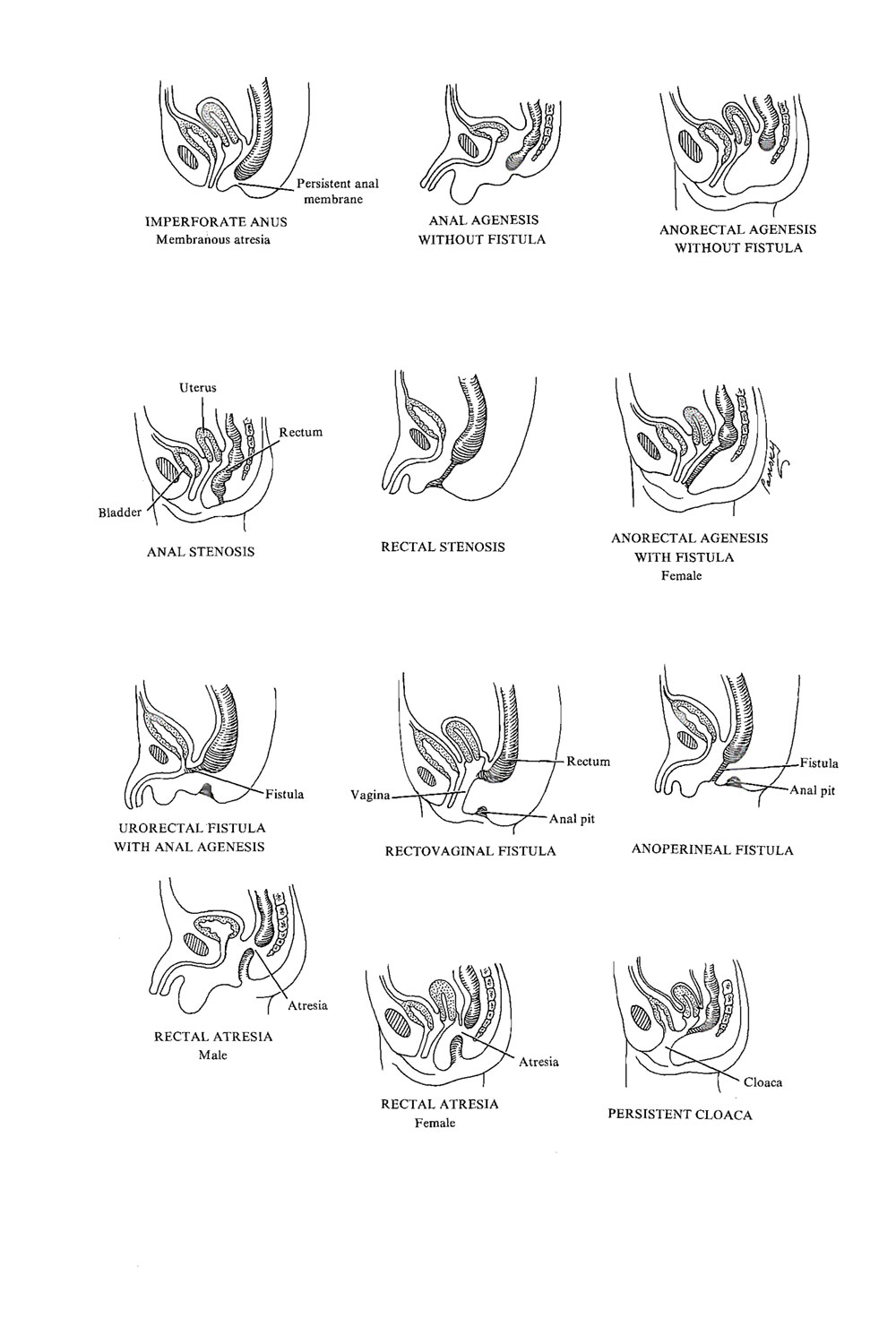
- Malformations of the hindgut: some form of imperforate anus is usually seen, occurs in 1/5000 births, and is more common in males. Most anorectal malformations result from an abnormal development of the urorectal septum, resulting in an incomplete separation of the cloaca into the urogenital and anorectal parts
- ANORECTAL MALFORMATIONS
- Clinically 3 major types are seen
- Imperforate anus or absent anus: classical anal imperfections include many varieties, and all require surgical intervention
- Insufficient anus leads to problems of meconium evacuation and should be treated without delay
- Ectopic sinus: less serious than (a) or (b) since it does allow some intestinal transport, but it, too, is usually functionally insufficient
- Developmental problems
- Superficial malformations; due to anomalies in formation and fixation at superficial perineal levels. Here we see
- Anal agenesis or insufficient anus (with or without fistula): the canal may end blindly, and there may be an ectopic opening (ectopic anus) or fistula opening in the perineum or vulva or male urethr Due to incomplete separation of the cloaca by the urorectal septum
- Membranous atresia or covered anus (with or without fistula): very rare; anus is in normal place, but a thin layer of tissue separates the anal canal from the exterior. Due to a failure of the anal membrane to perforate at the end of week 8
- Anorectal agenesis with or without fistula: rectum ends blindly above the anal canal, but there is usually a fistula to the urethra in the male or vagina in the femal The defect is similar to (i) above
- Deep malformations: where the anomaly affects septation of the cloaca by aberrant migration of the urorectal septum
- Pure rectal atresia: complete failure of the formation of the inferior part of the rectum and anal canal
- Rectal atresia with fistula: always insufficient. The length and degree of anastomosis differentiate the various types of anomaly
- Mixed malformations include all forms of ectopic anus
- May involve abnormal anastomoses of the anus to the perineum and reflect both perineal and cloacal abnormalities